代码整理器
2010年8月06日 23:55 | Comments(15) | Category:C语言 | Tags:c 转换
/*Neat Code v0.1 author:star date:2010
没有经过优化和维护,一次写成版本。为了方便地整理排版乱的代码。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void NeatSpace(FILE *fin, FILE *fout); //格式化空格字符
int NeatType(FILE *fin, FILE *fout); //格式化缩进
void Putlevel(FILE *out, int lv); //输出缩进
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FILE *fin, *fout;
char buf[255]= "t_";
int ErrorCode;
if(1 == argc)
{
printf("Neat Code v0.1 -- star\n\n");
printf("整理成Star喜欢的代码样式。\n");
printf("Usage:\nNeatCode source [destination]\n\n");
printf(" source 指定要整理的文件。\n");
printf(" [destination] 可生成的目标文件。\n\n");
printf("如果没有输入目标文件,将会生成默认的。\n");
}
else
if(2 == argc)
{
if(!(fin = fopen(argv[1], "r")))
{
printf("错误001 - 无法打开%s文件。", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fout = fopen("~TEMP.NTC", "w");
NeatSpace(fin, fout);
fclose(fin);fclose(fout);
fin = fopen("~TEMP.NTC", "r");
strncpy(buf+2, argv[1], 253);
if(!(fout = fopen(buf, "w")))
{
printf("错误002 - 创建%s文件失败。", buf);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
ErrorCode = NeatType(fin, fout);
fclose(fin);fclose(fout);
system("del ~TEMP.NTC");
if(ErrorCode) printf("错误005 - 所格式化的代码不标准 代码%d。", ErrorCode);
else printf("成功执行!");
}
else
if(3 == argc)
{
if(!(fin = fopen(argv[1], "r")))
{
printf("错误001 - 无法打开%s文件。", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fout = fopen("~TEMP.NTC", "w");
NeatSpace(fin, fout);
fclose(fin);fclose(fout);
fin = fopen("~TEMP.NTC", "r");
if(!(fout = fopen(argv[2], "w")))
{
printf("错误003 - 创建新的%s文件失败。", argv[2]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
ErrorCode = NeatType(fin, fout);
fclose(fin);fclose(fout);
system("del ~TEMP.NTC");
if(ErrorCode) printf("错误005 - 所格式化的代码不标准 代码%d。", ErrorCode);
else printf("成功执行!");
}else
{
printf("错误004 - 无效的命令。");
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
void NeatSpace(FILE *fin, FILE *fout)
{
char ch = fgetc(fin);
short cflag = 1;
while(!feof(fin))
{
if(ch == '/' && fputc(ch, fout) && (ch=fgetc(fin)))
{
if(ch == '/' && fputc(ch, fout))
while((ch=fgetc(fin)) != '\n') fputc(ch, fout);
else if(ch == '*' && fputc(ch, fout))
while((ch=fgetc(fin)) != '/') fputc(ch, fout);
}
if(ch == '\n' && (cflag = 1) && fputc(ch, fout))
{
ch = fgetc(fin);
while(!feof(fin) && ch == '\n' || ch == ' ' || ch == '\t') ch = fgetc(fin);
continue;
}
if(ch == ' ' || ch == '\t')
{
if(cflag == 0) fputc(ch, fout);
while(ch == ' ' || ch == '\t') ch = fgetc(fin);
continue;
}
else
{
if (ch != '{') cflag = 0;
do{fputc(ch, fout);ch = fgetc(fin);}
while(ch != '\n' && ch != ' ' && ch != '\t');
}
}
}
int NeatType(FILE *fin, FILE *fout)
{
char ch = fgetc(fin);
short IsTop = 1;
signed int level = 0;
if(ch == '\n') ch = fgetc(fin);
while(!feof(fin))
{
while(ch != '\n' && ch != '{' && ch != '}')
{
IsTop = 0;
fputc(ch, fout);
ch = fgetc(fin);
}
if(ch == '\n' && (IsTop = 1))
{
fputc(ch, fout);
ch = fgetc(fin);
if(ch != '}')
Putlevel(fout, level);
}else
if(ch == '{')
{
++level;
if(!IsTop) fputc('\n', fout);
while(ch = fgetc(fin))
if(ch == ' ' || ch == '\t');
else if(ch == '\n') {fputc('{', fout);break;}
else
{
Putlevel(fout, level-1);
fputc('{', fout);
fputc('\n', fout);
break;
}
Putlevel(fout, level);
}else
if(ch == '}')
{
--level;
if(!IsTop) fputc('\n', fout);
Putlevel(fout, level);
fputc('}', fout);
ch = fgetc(fin);
}
}
return level;
}
void Putlevel(FILE *out, int lv)
{
if(lv > 0)
while(lv--) fputc('\t', out);
}
上次不小心删了,再发一次吧。
求一个数是第几个排列数
2010年8月06日 00:47 | Comments(81) | Category:C语言 | Tags:c 数学 康托 排列组合 转换
根据康托展开公式: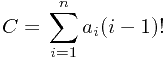
a[i]为第i个数比后面的都小的个数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int FAC[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880};
int CantorExp(char *s, int n)
{
int i, j, t, num = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
t = 0;
for(j = i+1; j < n; ++j)
if(s[j] < s[i])
++t;
num += FAC[n-i-1]*t;
}
return num+1;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char s[] = "1324"; //输入一个排列数的字符串序列
printf("%d", CantorExp(s, strlen(s)));
return 0;
}
求平面最近点对
2010年8月04日 03:33 | Comments(44) | Category:C语言 | Tags:c 数学 分治 平面点集
对于平面上N个点,求其中两个距离最近的点。输入格式:点的个数N,然后是N个坐标即可计算出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct pos {double x, y;};
typedef struct pos Pos;
Pos p[100000];
int d[100000];
double eps = 0.00001;
int cmp_x(const void *p, const void *q)
{
double tmp=((Pos*)p)->x-((Pos*)q)->x;
if(tmp>0) return 1;
else if(fabs(tmp)<eps) return 0;
else return -1;
}
double Dest(Pos p2, Pos p1)
{
return ((p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)+(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x));
}
double Min(double a, double b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return(*(int *)a-*(int *)b);
}
double NSP(int left, int right)
{
double m1, m2, m3 , res;
int i, j, ix, mid;
if(right - left == 1)
return Dest(p[right], p[left]);
else if(right - left == 2)
{
m1 = Dest(p[left], p[left+1]);
m2 = Dest(p[left], p[left+2]);
m3 = Dest(p[left+1], p[left+2]);
return Min(m1, Min(m2, m3));
}
mid = (left+right)/2;
res = Min(NSP(left, mid), NSP(mid+1, right));
ix = 0;
for(i = mid; i>=left && p[mid].x-p[i].x < res; --i)
d[ix++] = i;
for(i = mid+1; i<=right && p[i].x-p[mid+1].x < res; ++i)
d[ix++] = i;
qsort(d, ix, sizeof(d[0]), cmp);
for(i = 0; i < ix; ++i)
for(j = i+1; j<ix && j<i+4 && p[d[j]].y-p[d[i]].y < res; ++j)
res = Min(res, Dest(p[d[j]], p[d[i]]));
return res;
}
int main(void)
{
int N, i;
while(scanf("%d", &N), N)
{
assert(N!=1 && N<100000);
for(i = 0; i < N; ++i)
scanf("%lf %lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
qsort(p, N, sizeof(p[0]), cmp_x);
printf("%.2lf\n", sqrt(NSP(0, N-1)));
}
return 0;
}
用的是分治法。
求一个数的二进制有多少个1?
2010年8月03日 02:29 | Comments(1) | Category:C语言 | Tags:c 分治 位运算 二进制
/*author:Star date:2010-08-02*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
int CntBit(unsigned int n) //分治思想
{
n = ((n & 0xaaaaaaaa) >> 1 ) + (n & 0x55555555);
n = ((n & 0xcccccccc) >> 2 ) + (n & 0x33333333);
n = ((n & 0xf0f0f0f0) >> 4 ) + (n & 0x0f0f0f0f);
n = ((n & 0xff00ff00) >> 8 ) + (n & 0x00ff00ff);
n = ((n & 0xffff0000) >> 16) + (n & 0x0000ffff);
return n;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
unsigned int N;
int i, j;
scanf("%u", &N);
printf("%u:", N);
i = CntBit(N);
assert(i >= 0 && i <= 32);
for(j = 31; j >= 0; --j)
printf("%d", N&(1<<j) ? 1 : 0);
printf("\nhave %d bit that are \'1\'", i);
return 0;
}
这里数以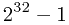 的大小范围为例。
的大小范围为例。
高精度除法器
2010年8月02日 02:41 | Comments(3) | Category:C语言 | Tags:c 数学 高精度 除法
/*高精度除法器 v0.1 Author:star date:2010
*可以计算无限循环小数,循环部分用括号表示
*因为整数除法最终肯定会循环,所以输出是有穷的
*一些例子:
*1/3 = 0.(3)
*22/5 = 4.4
*1/7 = 0.(142857)
*2/2 = 1.0
*3/8 = 0.375
*输入格式:数字1+/字符+数字2+回车
*输入例子:45/56
*输出结果:0.803(571428)
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <memory.h>
#define BIT 100000 //除数与被除数范围都为100000
int main(void)
{
int N, D, Mods[BIT+100];
char Ans[BIT+100];
int i, j, st, ed, mod, cnt, Flag, tp , bt;
char PreChar[100];
NEXT:
memset(Mods, 0, sizeof(Mods)); //初始化内存
memset(Ans, 0, sizeof(Ans));
memset(PreChar, 0, sizeof(PreChar));
scanf("%d/%d", &N, &D); //输入
assert(N >= 1 && N <= BIT); //输入限制的数字和范围
assert(D >= 1 && D <= BIT);
Mods[N] = cnt = Flag = 1; //初始化
if(!(N % D)) //整除了直接输出
{
printf("%d.0\n", N/D);
goto NEXT;
}
if(N < D) //计算小数点前
{
PreChar[0] = '0';
PreChar[1] = '.';
}
else
{
tp = N / D;
bt = log10(tp);
PreChar[bt+1] = '.';
for(i = bt; i >= 0; --i)
{
PreChar[i] = tp % 10 + '0';
tp /= 10;
}
N %= D;
PreChar[i] = '.';
}
i = 0;
mod = 100009; //Magic Number
while (!Mods[mod]) { //计算小数点后的除法
Mods[mod] = cnt;
++cnt;
N *= 10;
Ans[i++] = N / D + '0';
N = mod = N % D;
}
//寻找开始循环与结束循环
ed = cnt - 1;
st = Mods[mod];
//整除清0
if(Ans[ed-1] == '0' && Mods[0])
{
Flag = 0;
Ans[ed-1] = '\n';
}
//输出
printf("%s", PreChar);
for(j = 0,i = 1; i < st; ++i)
if(Ans[i-1])
printf("%c", Ans[i-1]);
if(Flag)
printf("(");
for(j = i; Ans[j-1]; ++j)
printf("%c", Ans[j-1]);
if(Flag)
printf(")\n");
goto NEXT;
}